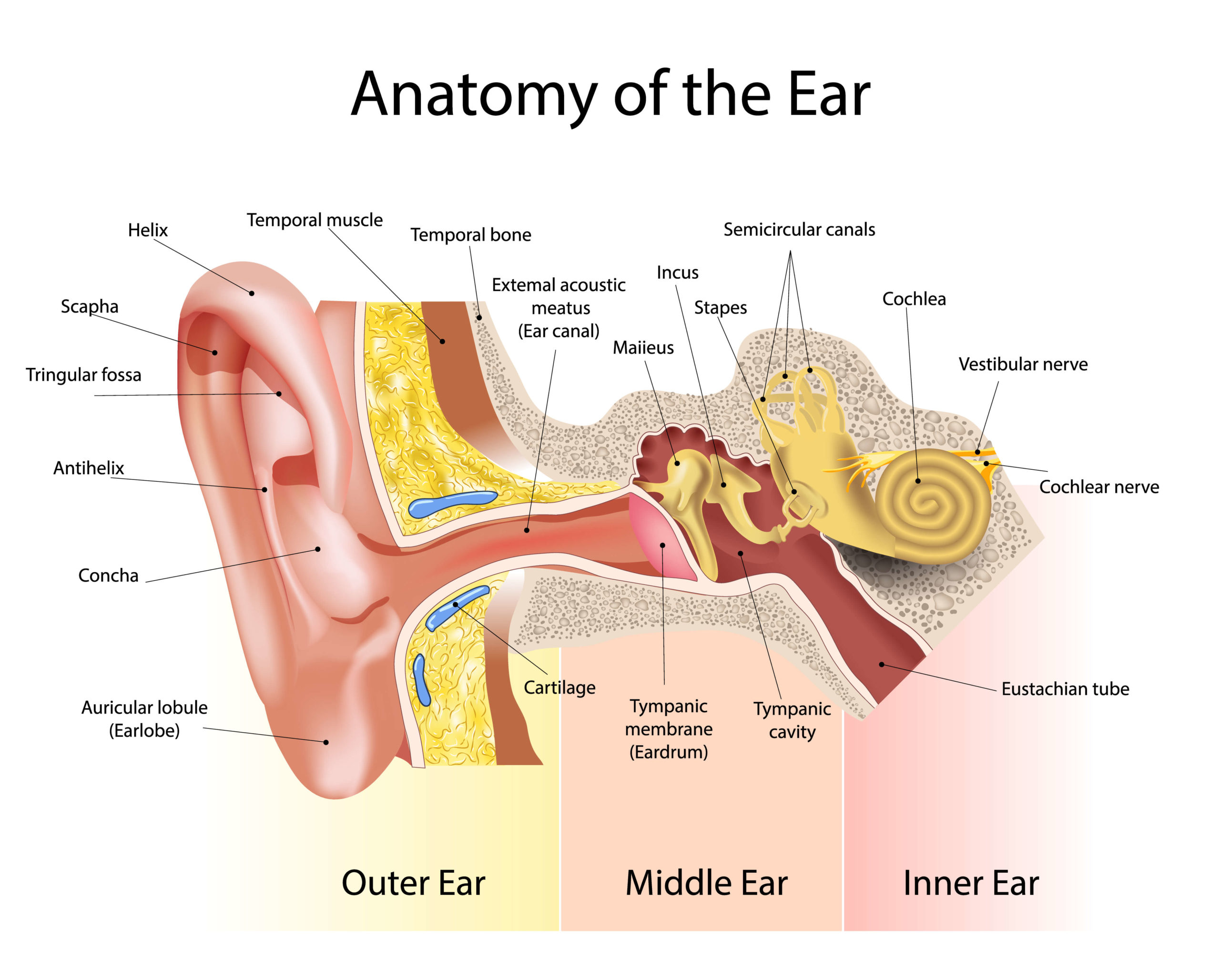
The ear controls hearing and balance and is made up of three parts–the outer, the middle, and the inner ear. All three parts of the ear are important for detecting sound–they work together to move sound from the outer part through the middle, and into the inner part of the ear.
The hearing mechanism in the human body is a highly sophisticated and robust system. Sound is transformed from pressure waves in the environment to mechanical energy. This is accomplished through a complex system of levels and area ratios. Through electrochemical reactions, this mechanical energy is transformed into something that the brain recognizes as music, warning signals, sounds of nature and meaningful conversation.
The Outer Ear funnels the sounds around us down to the eardrum. The outer ear is made up of the pinna (the ear that you see) and the ear canal. They act as resonators, which amplify certain pitches or frequencies of sound before they reach the eardrum.
The Middle Ear is where the sound is changed from pressure waves to mechanical energy. The eardrum (tympanic membrane) is made of layers of skin, which are stretched tight like the top of a drum. As sound enters the ear canal, the eardrum begins vibrating. Attached to the eardrum are three tiny bones called the Hammer (Malleus), Anvil (Incus) and Stirrup (Stapes). Their job is to transfer the vibration of the eardrum to hydraulic waves in the inner ear.
The Inner Ear is where the nerves pick up sound for delivery to the brain. Within the inner ear is the Cochlea, a fluid-filled bony labyrinth, which houses thousands of tiny hair cells. The hair cells work to detect the pitch of the pressure waves and convert them to electrical impulses that are transmitted to the hearing (auditory) nerve and up to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. The organ of balance is also found in the inner ear.
Sound waves reaching the outer ear cause the eardrum to vibrate. The vibrations are passed on from the middle ear to the inner ear. This is where the actual organ of hearing, the cochlea, is found. Fine hair cells in the cochlea play an important role in converting the sound waves into electrical signals.
Check out this video on Hearing and How It Works–it further illustrates how sounds travel from the ear to the brain where they are interpreted and understood.
Your hearing is a priceless commodity, so take care of it. Here are some things you can do to protect your hearing.
There are several things that can affect your hearing, but don’t necessarily cause permanent hearing loss. For example, earwax build-up in the ear canal can reduce sound transmission and your hearing in an ear. The presence of fluid in the eardrum (otitis media) can also cause temporary hearing loss by reducing movement of the eardrum and middle ear hearing bones. These issues are treatable and hearing can readily be restored with proper treatment.
Hearing loss affecting adults is typically associated with aging, but can also be due to hereditary factors, noise exposure (occupational and recreational), viral and bacterial infections, heart conditions or stroke, head injuries, tumors, and certain medications.
If you notice any changes to your hearing, contact Infinity Hearing at (207) 451-2700 to make an appointment with one of our audiologists. During your appointment, your audiologist will perform a comprehensive hearing evaluation and offer treatment recommendations that best meet your needs and lifestyle. To learn more about Infinity Hearing, please browse our website. You can also schedule an appointment online.